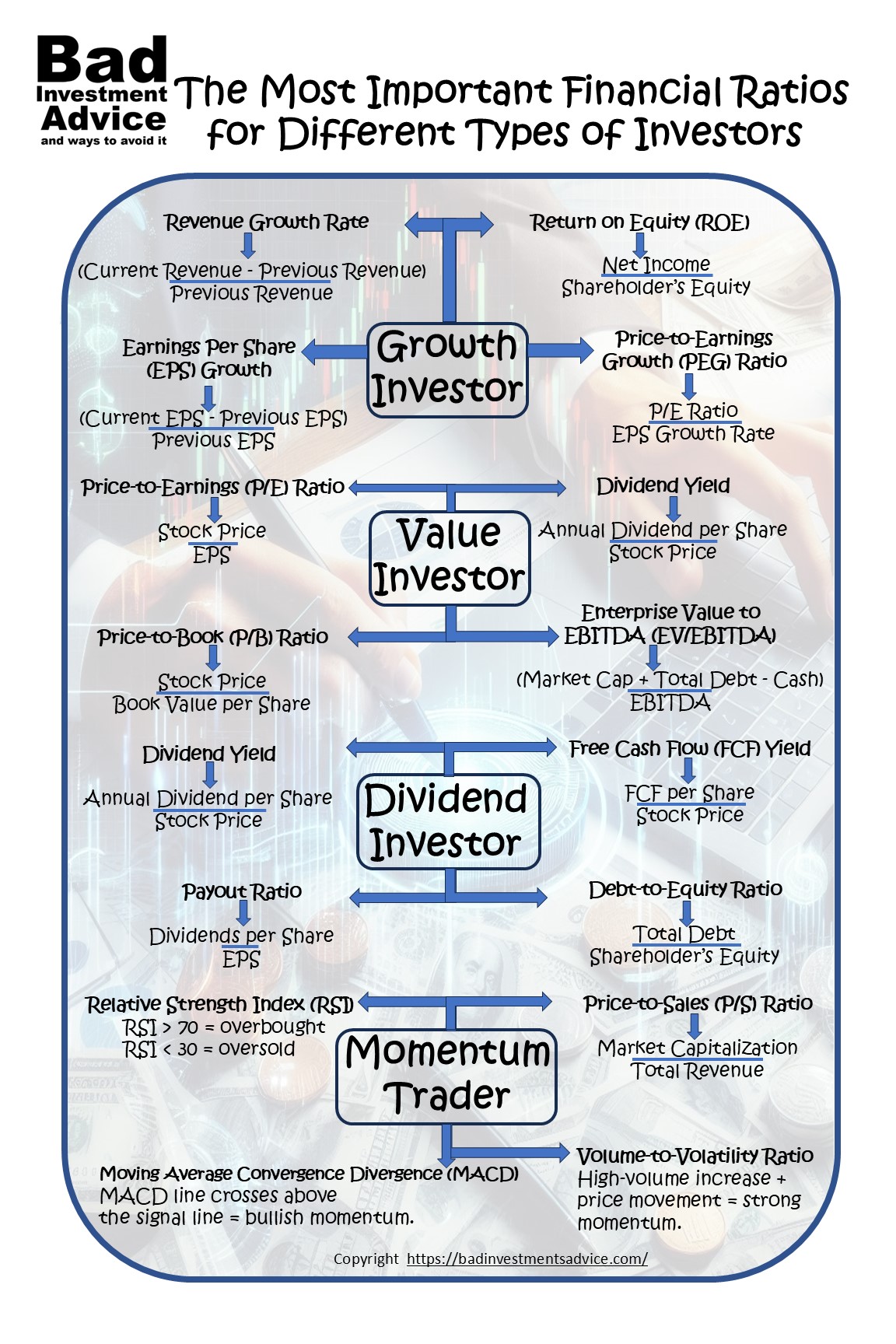
Investors have different strategies and goals when analyzing stocks, and the financial ratios they prioritize vary accordingly. Whether you’re a growth investor, a value investor, a dividend investor, or a momentum trader, understanding the right financial ratios can help you make informed decisions. In this guide, we’ll break down the most important financial ratios for each type of investor and explain how to use them effectively.
Investors have different strategies and goals when analyzing stocks, and the financial ratios they prioritize vary accordingly. Whether you’re a growth investor, a value investor, a dividend investor, or a momentum trader, understanding the right financial ratios can help you make informed decisions. In this guide, we’ll break down the most important financial ratios for each type of investor and explain how to use them effectively.
You’ll notice that some of these ratios relate to the business fundamentals of the company, whereas others relate more to price movements.
There’s no surprise here. Long-term investors are more concerned with business fundamentals, the rationale being, if the fundamentals are strong the market will come to appreciate and bid up the price.
Short-term traders are more interested in profiting from price momentum or price reversals so they are more focused on price movements or technicals.
Growth Investors: Which Ratios Matter Most?
Growth investors seek companies that demonstrate strong revenue and earnings expansion. The following financial ratios are key indicators of a company’s potential for future growth:
- Revenue Growth Rate: Measures how fast a company’s sales are increasing over time.
- Formula: (Current Revenue – Previous Revenue) / Previous Revenue
- A high revenue growth rate suggests strong market demand and competitive advantage.
- Earnings Per Share (EPS) Growth: Indicates how much profit is allocated to each outstanding share.
- Formula: (Current EPS – Previous EPS) / Previous EPS
- Consistent EPS growth signals increasing profitability.
- Return on Equity (ROE): Shows how effectively a company generates profits from shareholder equity.
- Formula: Net Income / Shareholder’s Equity
- A high ROE suggests efficient capital utilization.
- Price-to-Earnings Growth (PEG) Ratio: Adjusts the P/E ratio by factoring in earnings growth.
- Formula: P/E Ratio / EPS Growth Rate
- A PEG ratio below 1 may indicate an undervalued growth stock.
Value Investors: How to Find Undervalued Stocks Using Ratios
Value investors focus on finding stocks that are undervalued compared to their intrinsic worth. The following ratios are essential for identifying potential bargains:
- Price-to-Earnings (P/E) Ratio: Compares stock price to earnings per share.
- Formula: Stock Price / EPS
- A lower P/E suggests that the stock may be undervalued.
- Price-to-Book (P/B) Ratio: Compares a stock’s market value to its book value.
- Formula: Stock Price / Book Value per Share
- A P/B ratio below 1 indicates that a stock may be trading below its intrinsic value.
- Dividend Yield: Represents the annual dividend payment as a percentage of stock price.
- Formula: Annual Dividend per Share / Stock Price
- A high dividend yield can signal a potentially undervalued stock, though caution is needed.
- Enterprise Value to EBITDA (EV/EBITDA): Evaluates a company’s total valuation in relation to its earnings. EBITDA stands for Earnings Before Interest, Taxes, Depreciation, and Amortization. It therefore looks at earnings from operations.
- Formula: (Market Cap + Total Debt – Cash) / EBITDA
- A low EV/EBITDA ratio may indicate an attractive buying opportunity.
 Dividend Investors: Ratios That Help Assess Stable Income Investments
Dividend Investors: Ratios That Help Assess Stable Income Investments
Dividend investors prioritize income stability and yield. The following ratios help assess the reliability of a company’s dividend payments:
- Dividend Yield: Measures the percentage return from dividends relative to stock price.
- Formula: Annual Dividend per Share / Stock Price
- A high dividend yield is attractive, but it should be sustainable.
- Payout Ratio: Indicates the proportion of earnings paid as dividends.
- Free Cash Flow (FCF) Yield: Shows how much cash flow is available after capital expenditures.
- Debt-to-Equity Ratio: Measures financial leverage and risk.
- Formula: Total Debt / Shareholder’s Equity
- A low ratio suggests the company has manageable debt and can sustain dividend payments.
Reliable dividend paying stocks are often in capital intensive, highly regulated industries. A dividend investor is going to want to check that there are no foreseeable disruptions to the company’s ability to continue paying dividends. Check that the company continues to invest in plant and that its industry is healthy overall. It will also pay to check whether any regulatory changes could place unanticipated demands on the company’s finances.
Momentum Traders: Using Valuation and Liquidity Ratios to Spot Trends
Momentum traders seek stocks with strong price movements and trading volume. This is where technical indicators of stock price movements are more relevant. The following ratios can help identify breakout opportunities:
- Relative Strength Index (RSI): Measures the speed and change of price movements.
- RSI above 70 suggests overbought conditions; below 30 indicates oversold conditions.
- Moving Average Convergence Divergence (MACD): Tracks momentum and trend direction.
- When the MACD line crosses above the signal line, it suggests bullish momentum.
- Price-to-Sales (P/S) Ratio: Compares a company’s market cap to its revenue.
- Formula: Market Capitalization / Total Revenue
- A low P/S ratio may indicate an undervalued stock with growth potential.
- Volume-to-Volatility Ratio: Measures how trading volume changes with price movements.
- A high volume increase with price movement may signal strong momentum.
How Each Type of Investor Should Weigh Different Ratios
Each investor type must balance different financial ratios based on their strategy:
- Growth Investors: Prioritize revenue and earnings growth, ROE, and PEG ratio.
- Value Investors: Focus on P/E, P/B, EV/EBITDA, and dividend yield.
- Dividend Investors: Assess dividend yield, payout ratio, free cash flow, and debt levels.
- Momentum Traders: Use RSI, MACD, trading volume, and P/S ratio for trend identification.
 Final Thoughts
Final Thoughts
Understanding and using financial ratios effectively can help investors make better decisions based on their goals. Growth, value, dividend, and momentum investors all use different ratios, but a well-rounded approach that considers multiple factors can provide deeper insights.
By focusing on the right financial ratios for your investing style, you can increase your chances of making sound investment decisions and maximizing returns over time.
Next Steps:
- Download our Investor Ratio Cheat Sheet
- Learn more about Advanced Stock Analysis Techniques
- Subscribe for more investment insights!
Affiliate Disclosure: This article contains affiliate links. If you click on a link and buy something, I may receive a commission. You will pay no more so please go ahead and feel free to make a purchase. Thank you!
It has often been said that there is no better investment than your own financial education. One great way to accelerate your financial education and your investing success is with the American Association of Individual Investors, the AAII. When you join the AAII, you get access to reports, courses on investing, risk management, asset allocation, retirement planning, managing retirement finances, and other resources, all for a single annual membership fee.
Single-page Summary
Here is a single-page summary of The Most Important Financial Ratios for Different Types of Investors. You can download a pdf here.
I hope you found this article interesting and useful. Do leave me a comment, a question, an opinion, or a suggestion and I will reply soonest. And if you are inclined to do me a favor, scroll down a bit and click on one of the social media buttons, and share it with your friends. They may just thank you for it.
You can also subscribe to email notifications. We will send you a short email when a new post is published.
Disclaimer: I am not a financial professional. All the information on this website and in this article is for information purposes only and should not be taken as personalized investment advice, good or bad. You should check with your financial advisor before making any investment decisions to ensure they are suitable for you.
Affiliate Disclosure: This article contains affiliate links. If you click on a link and buy something, I may receive a commission. You will pay no more so please go ahead and feel free to make a purchase. Thank you.